Back to the Basics: Poison Ivy (Toxicodendron) Dermatitis
Mon, 06/12/2017 - 5:00am
Editor:
Exposure results from contact with one of the following 3 plants:
o Toxicodendron radicans (Poison Ivy)

o Toxicodendron toxicarium (Poison Oak)

o Toxicodendron vernix (Poison Sumac)

- The Toxin: Urushiol (oo-RUE-shee-ohl) – oil based
- Effect: Type IV hypersensitivity reaction, causing a well-demarcated vesicular rash, occasionally associated with bullae. The rash is intensely pruritic and may occur in streak-like patterns from brushing up against the offending agent
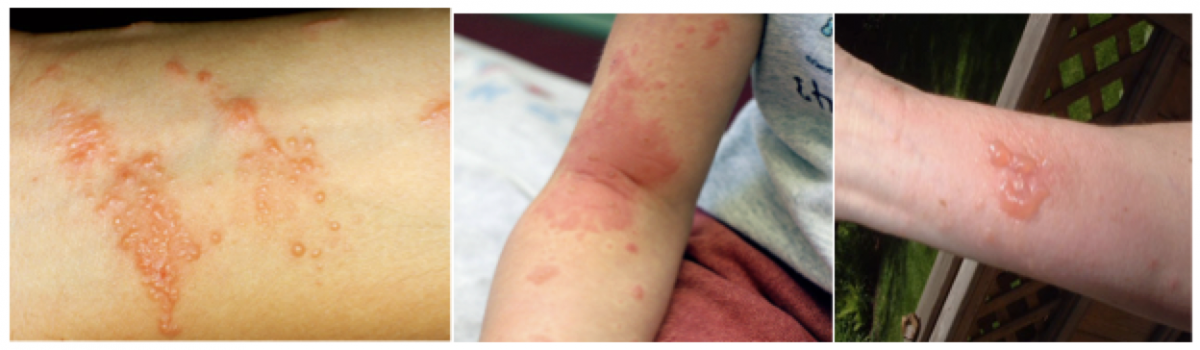
- Considered a Severe Reaction if:
- 20% of body surface area covered
- Involves:
- Face
- Hands
- Feet
- Genitals
- Treatment:
- Immediate decontamination with soap and water
- Symptomatic control with:
- ice, calamine lotion
- Steroid cream
- Oral steroids for severe cases and for those with marked discomfort – Strongly suggest a 2-3 week taper starting with a dose of 1 mg/kg/day (max dose of 60 mg) to prevent rebound rash that common occurs with medrol dose pack or other short courses of steroids
- Zanfel – an over the counter, topical product composed of surfactants that bind the uroshiol oil for easier washing after initial exposure. There is not yet data to support its use at this time
References
- Nelson, Lewis S., Lewin, Neal A., Howland, Mary Ann, Hoffman, Robert S., Goldfrank, Lewis R., Flomenbaum, Neal E. Goldfrank’s Toxicologic Emergencies, 9th Edition. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2011. Print.
- Curtis, G., Lewis, A. Treatment of Severe Poison Ivy: A Randomized, Controlled Trial of Long Versus Short Course Oral Prednisone. J Clin Med Res. 2014; 6(6):429-34
- Prok, L., McGovern, T. Poison ivy (toxicodendron) dermatitis. Uptodate.com. Accessed June 11, 2017.
