Board Review: Internal Medicine
30 year old with past medical history of an ovarian cyst who presents with palpitations and confusion. As per husband, the patient was complaining of abdominal pain 2 weeks prior and was seen in the emergency department found to have cholelithiasis on CT abdomen and pelvis with IV contrast. Vitals are as follows: T: 102.4; HR: 140; RR: 20; SpO2: 98 on RA. On exam, the patient is only oriented to person. Patient also has a mass on the anterior aspect of her neck without cervical adenopathy. On EKG, patient has an irregular rhythm. On labs, TSH: 0.1 mu/L T4: 4.00 ng/dL. What phenomenon is responsible for patient’s underlying condition?
-
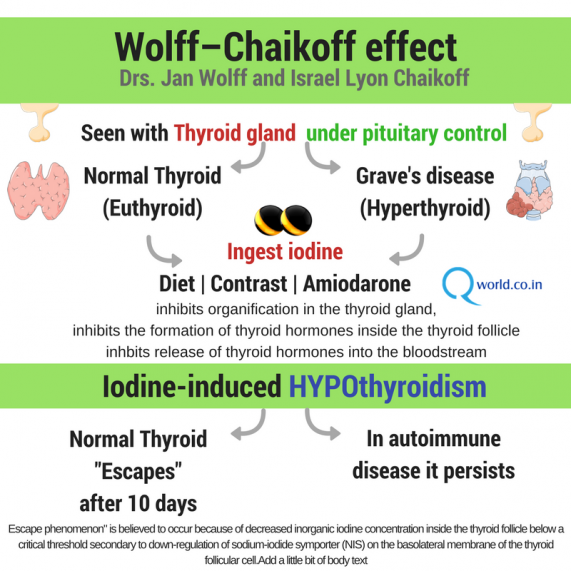
Wolff-Chaikoff Phenomenon
-
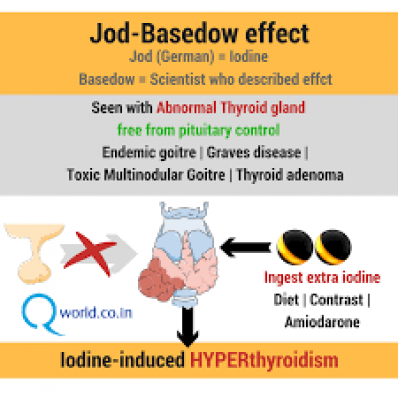
Jod-Basedow Phenomenon
-
Somogyi Phenomenon
-
Dawn Phenomenon
-
Gallavardin Phenomenon
Answer: B. This patient has a goiter and this phenomenon is seen after iodinated load which can be from exogenous supplementation or contrast. The phenomenon results from failure of autoregulation of the thyroid gland. Patients usually have underlying subclinical hyperthyroidism, and when exposed to an iodine load in excess, instead of blocking the organification process, the thyroid gland (areas of autonomously functioning gland) continues to uptake the iodine producing more thyroid hormone independent of normal regulatory mechanisms.
References
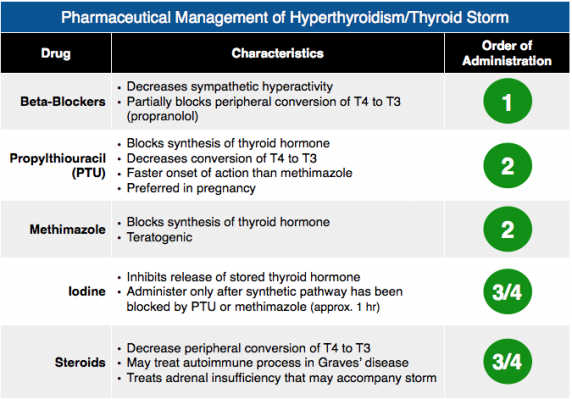
Gupta, Nachi. “Pharmaceutical Management of Hyperthyroidism/Thyroid Storm.” Rosh Review. June 2017. <www.roshreview.com>.
Qworld. “Jod Basedow Effect.” <www.qworld.co.in> March 2018. Date accessed 11/14/20.
Qworld. “Wolff- Chaikoff Effect.” <www.qworld.co.in> March 2018. Date accessed 11/14/20.
Surk, M. “Iodine-Induced Thyroid Dysfunction.” April 2019. <www.uptodate.com>. Date Accessed 11/14/20.
