Board Review: Internal Medicine
A 75 yo female with hypothyroidism presents to the ED with lethargy. She is hypothermic, hypotensive, and bradycardic. Further testing reveals hyponatremia and hypoglycemia. On exam, you note non-pitting edema localized to the face, tongue, and hands. TSH is high and T4 is very low. What is the most important treatment for this patient at this time?
-
Corticosteroids
-
Broad spectrum antibiotics
-
30cc/kg crystalloid IVF
-
Thyroid hormone
Answer: D. This presentation is consistent with myxedema coma, a hypothyroid emergency with a high mortality rate. This condition can arise in a poorly controlled longstanding hypothyroid patient or can be triggered by an acute event such as infection or surgery in a patient with a history of hypothyroidism. Thyroid hormone - T4 and T3 - should be given promptly for this diagnosis, in addition to continued supportive care (which may include intubation). Steroids will be given as well provided that coexisting adrenal insufficiency is still a possibility and sepsis will also be in your differential. Keep an eye out for myxedema coma in patients taking lithium or patients presenting with a pericardial effusion as well!
Check out this chart on myxedema coma from a prior EMDaily #EMConf post in 2018:
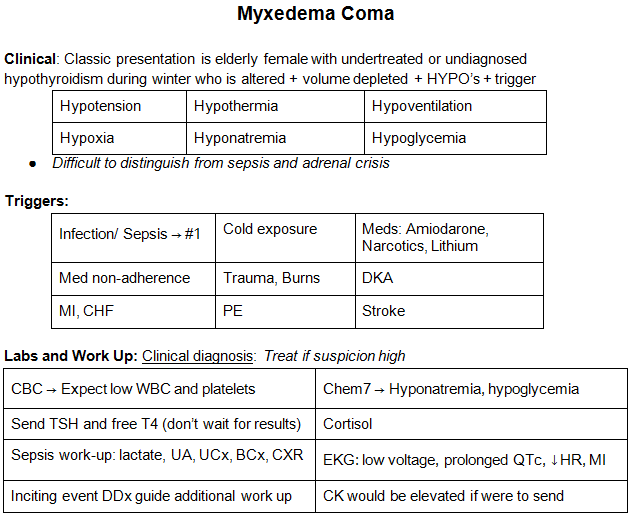
References:
Kwaku MP, Burman KD. Myxedema coma. J Intensive Care Med. 2007 Jul-Aug;22(4):224-31. doi: 10.1177/0885066607301361. PMID: 17712058.
