What's the diagnosis? By Dr. Abby Renko
A 39 yo male presents to the ED with change in mental status and tachypnea. Per family has been ongoing for about a month but memory particularly bad in the last few days. He is an alcoholic who was born in Mexico but has lived in the US for the last 20 years.
On arrival to the ED, he is febrile to 102 and hypoxic, requiring high flow oxygen therapy. Initial lab work reveals hyponatremia and transaminitis. CT head is unremarkable. A CT chest is shown as well as MRI brain. What's the diagnosis? Scroll down for answer.
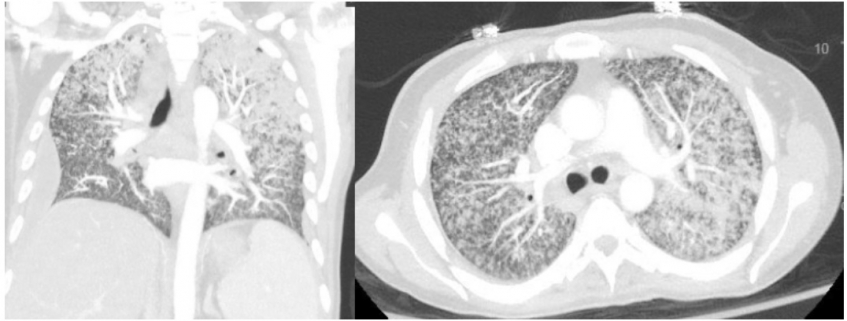
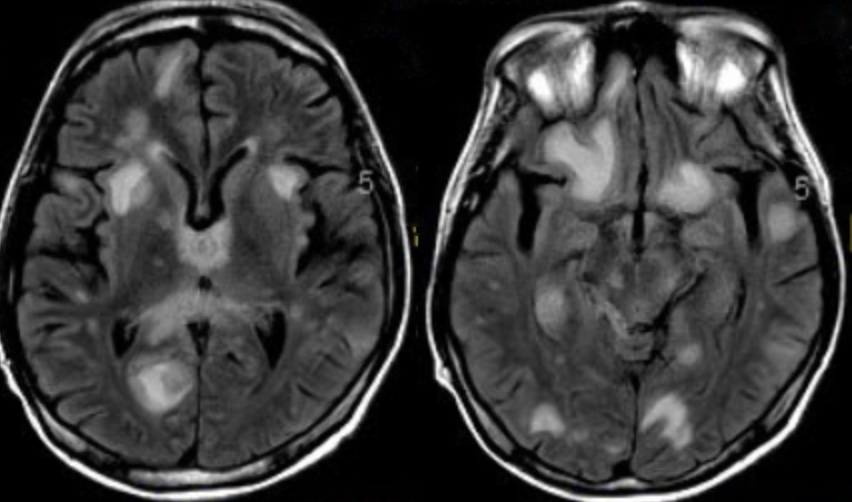
Answer: Miliary (disseminated) tuberculosis
- Mycoplasma tuberculosis affects 1/3 of the world's population
- Risk factors: immigraion from or living in a country with high prevalance of disease, close contact with infected persons (crowded living facilities (shelters, jails), immunocompromised, older age, substance or tobacco abuse, malnutrition, systemic disease (silicosis, diabetes, renal failure), healthcare worker
- Types of TB
- Primary
- typically asymptomatic
- sometimes community aquired pneumonia symptoms
- diagnosis
- chest xray with regional infiltrate and lymphadenopathy (Ghon complex)
- PPD +1-2 months after exposure
- Latent
- asymptomatic with +PPD
- diagnosis - PPD or IGRA if history of BCG vaccine
- Reactivation of disease
- pulmonary
- upper lobe infiltrate +/- cavitation
- extrapulmonary
- lymph nodes (most common)
- pleura - pleural effusion
- GU tract - UTI, pyelonephritis
- meninges - meningitis
- bone - Pott's disease, osteomyelitis, arthritis
- miliary - disseminated
- Treatment
- Latent
- 6-9 months of isoniazid (INH) or
- 3 months of INH + rifapentine
- Active / miliary
- INH (side effects: hepatitis, sideroblastic anemia, neuropathy, SLE)
- Rifampin (side effects: orange urine)
- Pyrazinamide (side effects: hyperuricemia)
- Ehambutol (side effects: optic neuritis)
- Meningitis and or pericarditis
- add corticosteroids - typically an 8 week dexamethasone taper
In this patient's case, her received the 4 drug regimen and corticosteroids with eventual improvement in mental status and respiratory function over the course of several months.
References:
-
Tintinalli, JE. Tintinalli's Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide. 8th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education LLC, 2016.
-
Blok B,Cheung DS, Platts-Mills TF. First Aid for the Emergency Medicine Boards. 3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education, LLC, 2016.
-
Garg RK. Central nervous system tuberculosis: Treatment and prognosis. In UpToDate, 5 Jan 2021.
